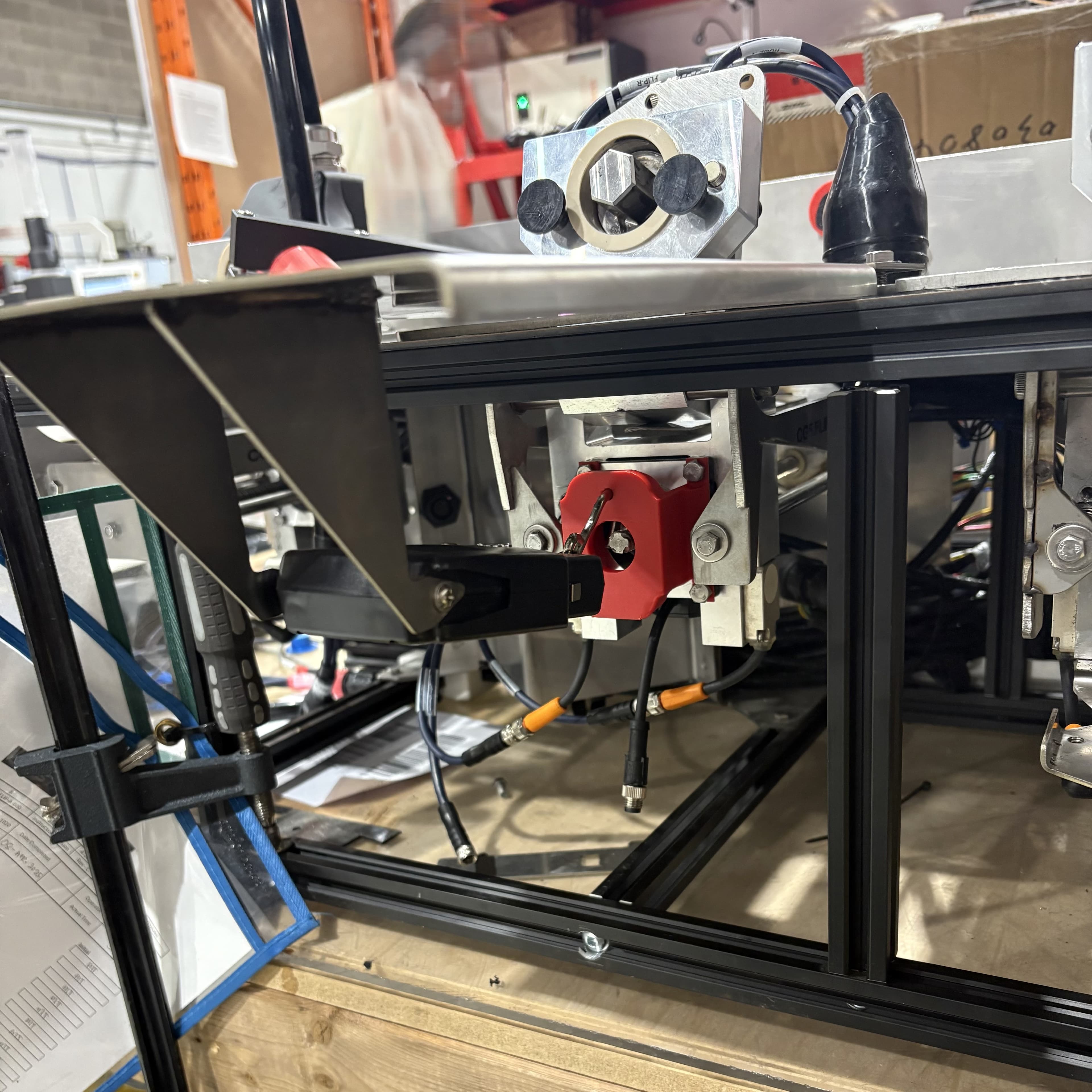
Motor Stall Force Test Fixture








Objective
Evaluate three coating types (DLC, TiN, Chrome) on SS304 lead screws and guide rods with 2-2.5μm coating thickness to quantify friction reduction to determine cost-benefit viability for production-scale coating implementation across all sub-mechanisms.
Process
- Developed linear actuator force measurement fixture:
- SolidWorks design
- Laser cut sheet metal
- Press brake forming
- Tack and filler welding to strengthen joints
- Comparing DLC, TiN, Chrome coatings vs uncoated SS304 baseline across polymer and bronze bushing combinations to identify lowest friction (motor current reduction), highest durability (extended runtime), and best grease resistance
- Established 9 quantitative metrics tracked with/without honey: rod diameter, bearing ID, initial/final linear force, motor current, run time to failure, motor temp, shaft temp
Result
Initial testing identified promising coating combinations with improved pull force. However, week-long stress testing revealed that the coatings peel off after 2 days due to the high friction, indicating that alternative material systems or design modifications are required.






